The percentage of Americans age 65 and older remains high, at 26.8%, or 14.3 million seniors (diagnosed and undiagnosed).
WHAT IS DIABETES?
Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a group of chronic conditions that cause high levels of sugar to build up in the blood, resulting in adverse health effects such as heart, eye and kidney disease. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), about 86 million US adults-more than a third-have prediabetes, and 90% of them don't know it. With prediabetes on the rise, it is important to be informed and educated about this chronic disease.Common types of diabetes include:
Type 1 Diabetes: In type I diabetes, is a complex genetic disease where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Without insulin, the glucose (sugar) flowing through the blood stream is unable to enter cells and remains in the blood. This type of diabetes was formerly referred to as insulin dependent, or juvenile onset diabetes since it most commonly develops in childhood or early adolescence. Type 1 diabetes is not preventable. Five-percent of people with diabetes have this form of the disease.
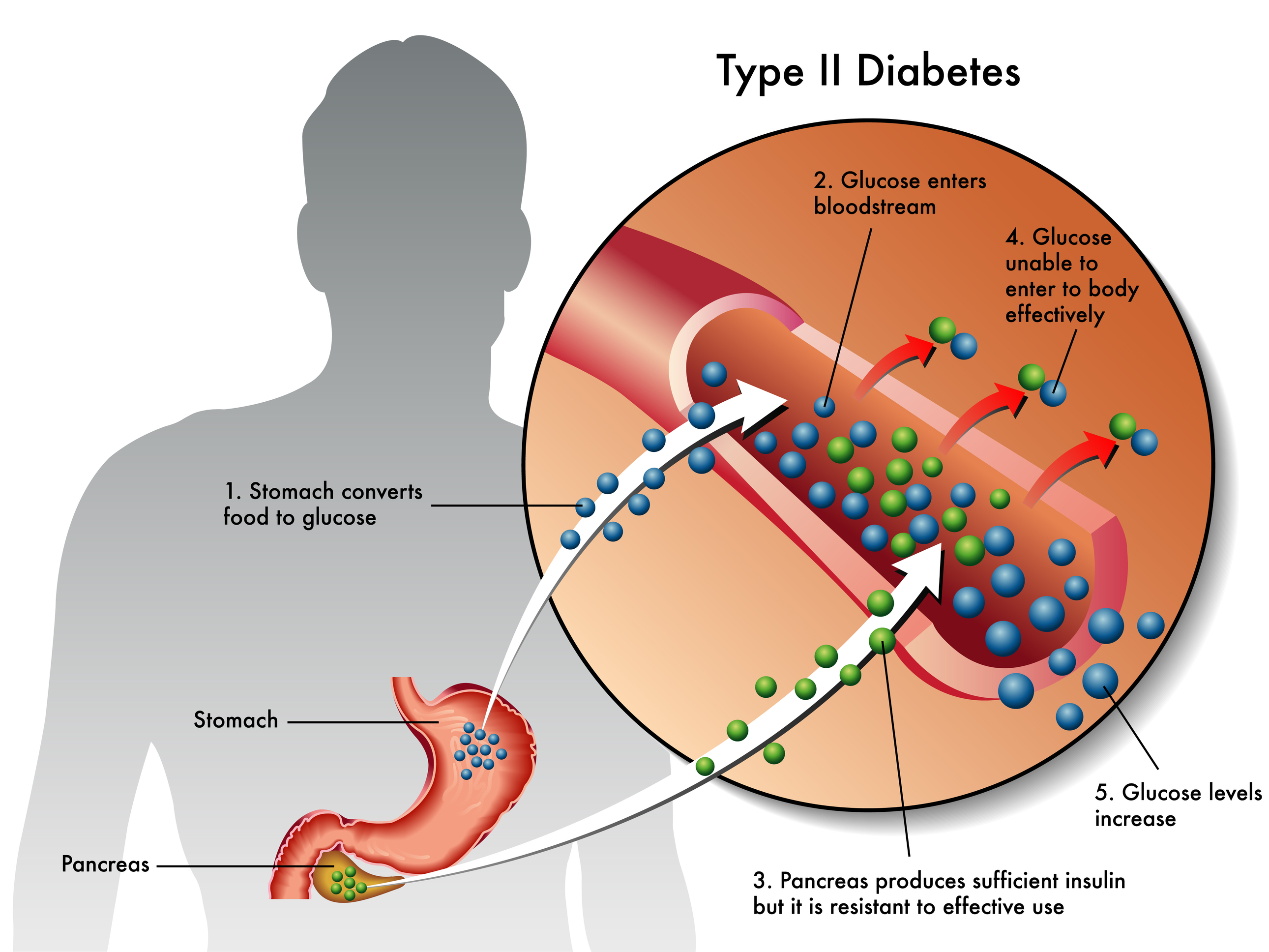
Type 2 Diabetes: In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas does produce insulin, but the cells are resistant to it. Doctors refer to this as insulin resistance. The glucose remains in the blood since it is unable to enter cells. This form of diabetes is preventable and is most often seen in individuals over 45 who are overweight or lead a sedentary lifestyle. Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes: According to the ADA (American Diabetes Association), gestational diabetes develops in about 9.2% of women during pregnancy. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is understood that the same hormones from the placenta that help the baby develop can also block the action of the mother's insulin in her body. This is another case of insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes starts when your body is not able to make and use all the insulin it needs for pregnancy. Most of the time it goes away after the baby is born. However, women that had gestational diabetes are at a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Prediabetes: Prediabetes is a condition when blood sugar levels are abnormally high but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. It is an early warning sign for the development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD), which can lead to heart attack or stroke. Find out more at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
WHY DOES IT HAPPEN?
Understanding how your body uses blood sugar for energy is important to understanding diabetes. After ingesting foods, the body breaks down the sugars and starches you eat into a simple sugar called glucose, which it uses for energy. The key to getting sugar into the cells of our body is the hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. If your body does not produce enough insulin, or if the body is resistant to insulin, glucose cannot reach the cells and will build up in the blood. Over time, this glucose build up in the blood leads to diabetes. Although diabetes has no cure, managing diabetes is possible for a long and healthy life.
As of 2014, 29.1 million people in the United States, or 9.3 percent of the population, had diabetes. More than 1 in 4 of them didn't know they had the disease. Diabetes affects 1 in 4 people over age of 65.
Return to top...
WHO IS AT RISK?
With 1.4 million people diagnosed with diabetes each year, recent studies reveal that up to 25% of people may be living with diabetes and not know it. Early stages of diabetes may not present obvious symptoms so it is important to understand the genetic and lifestyle factors that put an individual at risk for developing diabetes. Although a chronic illness, diabetes is manageable and individuals with diabetes are able to live a healthy and happy life.Risk Factors for Type I Diabetes
The precise cause of type I diabetes is unknown. It is a complex genetic disorder that is most common among children and young adults that have a family history of type 1 diabetes. About 5-10% of those diagnosed with diabetes have type 1. Unlike type 2 diabetes which can be brought on by lifestyle choices, individuals with type 1 diabetes are not responsible for its development. New research is uncovering the multitude of factors that can put someone at risk for type 1 diabetes. Factors that increase an individual's risk include:
- Family History - An individual with a parent or sibling that has type 1 diabetes.
- Genetics - Disorders in autoimmune function increase risk of type 1 diabetes. There are now 20 insulin-dependent genes that are associated with the development of diabetes.
- Race - Whites are more likely than blacks, Asian or Hispanic people to have type 1 diabetes.
- Illness - Recent studies show exposure to certain viruses in infancy can increase risk.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more common, with 90-95% of people with diabetes having type 2. It usually develops slowly over time and later in life. Researchers don't fully understand why some people develop prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and others don't. In 2012, 86 million American's had prediabetes, an increase of 79 million since 2010.
Factors that increase risk include:
- Age - Being over 45 years old. Although type 2 diabetes is increasing dramatically among children, adolescents and younger adults.
- Family History or Personal History - Having a family history of diabetes, prediabetes (abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood) or having gestational diabetes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome - Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (a common condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth and obesity).
- High blood pressure - Blood pressure over 140/90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg.)
- Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels - Low levels of HDL( "good" cholesterol) increases your risk of type 2 diabetes. Triglycerides are another type of fat carried in the blood. People with high levels of triglycerides have an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Weight - Being overweight (BMI>25) and/or excess body fat around the stomach. The more fatty tissue you have, the more resistant your cells become to insulin.
- Diet - Having a poor diet, or consuming large amounts of sugar.
- Inactivity - Leading a sedentary lifestyle (little or no regular physical activity).
- Race - For reasons unknown, African Americans, Hispanic Americans, Native Americans and Asian Americans are at greater risk.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Any pregnant woman can develop gestational diabetes, although some women are at greater risk than others.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Age - Women older than age 25 and pregnant.
- Family or personal history - Your risk increases if you have prediabetes or if a parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes. You're also at greater risk if you had gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy, if you delivered a very large baby or if you had an unexplained stillbirth.
- Weight - Being overweight before pregnancy.
- Race - Black, Hispanic, American Indian or Asian Americans are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Return to top...
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Diabetes is often called the "silent killer" because symptoms for type 2 diabetes can come on so subtly that an individual may not know anything is wrong. In general, the symptoms of type 1 diabetes come on more quickly and severe. Excessive thirst, frequent urination, sudden weight loss and extreme fatigue are among the four most common signs and symptoms of diabetes and anyone experiencing these symptoms should consult their doctor.Symptoms of Diabetes
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Extreme fatigue
- Irritability
- Blurred vision
- Cuts/bruises that are slow to heal
- Sudden weight loss - even though you are eating more (type 1)
- Tingling, pain, numbness in hands/feet (type 2)
Women with gestational diabetes often have no symptoms. Most doctors will recommend that pregnant women be tested for it at the proper time during pregnancy.
Two tests are commonly used to diagnose gestational diabetes. The first test is the initial glucose challenge test. The pregnant patient will drink a syrupy glucose solution and one hour later, will have a blood test to measure blood sugar level. A blood sugar level below 130 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) is usually considered normal. If blood sugar level is higher than normal, it means an increased risk for gestational diabetes in which case a follow up test called a glucose tolerance test will be administered at a later date. The follow-up glucose tolerance test requires the pregnant patient to fast overnight. They will have blood sugar level measured and then drink another sweet solution - this one containing a higher concentration of glucose. Blood sugar levels will be checked every hour for three hours. If at least two of the blood sugar readings are higher than normal, a patient will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
Other Serious Warning Signs Related to Diabetes -- Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) occurs when blood sugar (glucose) levels fall below normal. It is important for all patients with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia as they work to manage their blood sugar levels:
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Hunger
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion
Return to top...

COMPLICATIONS
Managing diabetes requires new habits for healthier living and a commitment to monitoring blood sugar levels. As difficult as it may be for some people to manage their diabetes, the consequences of not doing so are quite scary. The longer a person lives with diabetes that goes uncontrolled, the higher the risk of complications. Because the damage increased blood glucose levels have on the body develops gradually over time, those with diabetes may not feel the harm being done. Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. Possible complications include:A national survey of nearly 3,000 men and women diagnosed with eating disorders, showed that:
- Cardiovascular Disease - Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems. Those with diabetes are two to four times more likely to develop heart disease and two to four times more likely to experience a stroke.
- Nerve Damage (neuropathy) - Excess sugar can injure nerves, especially in the legs. This can cause tingling and numbness in toes or fingers and even the loss of all sense of feeling. Damage to the nerves related to digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. For men, it may lead to erectile dysfunction.
- Kidney Damage (nephropathy) - Diabetes can damage the kidneys' delicate filtering system leading to kidney failure or irreversible kidney disease requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Eye Damage (retinopathy) - Diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), potentially leading to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
- Foot damage - Nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow to the feet increases the risk of various foot complications. Cuts and blisters can develop serious infections, which often heal poorly. These infections may ultimately require toe, foot or leg amputation. About 60% of non-traumatic lower-limb amputations among people aged 20 years or older occur in people with diagnosed diabetes.
- Skin conditions - Diabetes may leave skin more susceptible to problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.
- Hearing impairment - Hearing problems are more common in people with diabetes.
Most women with gestational diabetes deliver healthy babies. However, untreated or uncontrolled blood sugar levels can cause problems for mother and baby. Complications that can occur include:
- Preeclampsia - This condition characterized by high blood pressure, excess protein in the urine, and swelling in the legs and feet, can lead to serious or even life-threatening complications for both mother and baby.
- Subsequent Gestational Diabetes - A woman that has had gestational diabetes once is more likely to have it again with the next pregnancy.
- Excess Baby Growth - Extra glucose from the mother can trigger extra insulin production in the baby, causing the baby to grow too large. Very large babies are more likely to require a C-section birth.
- Low Blood Sugar in Babies - Sometimes, shortly after birth, babies of mothers with gestational diabetes develop low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- Type 2 Diabetes Later in Life - Both mother and baby have a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Death - Untreated gestational diabetes can result in a baby's death either before or shortly after birth.
Prediabetes, a condition of higher than normal blood glucose levels, may develop into type 2 diabetes.
Return to top...

PREVENTION & MANAGEMENT
Although type 1 diabetes is a complex genetic autoimmune disease that cannot be prevented, it is possible to prevent type 2 diabetes, and reverse prediabetes, by maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle. For those diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it is important to manage the disease to avoid long-term complications by keeping blood glucose level in a healthy range through meal planning, physical activity, and medications.Prevention
Manage Your Weight - Managing body weight reduces the levels of glucose in the blood. Less fat allows the pancreas to secrete insulin more efficiently. Too much fat interferes with insulin production and makes it more difficult for glucose to leave the blood stream and enter cells where it will be used as energy.
Quit Smoking - Smokers are roughly 50 percent more likely to develop diabetes than nonsmokers, and heavy smokers have an even higher risk.
Exercise - The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends two hours and 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, like brisk walking, every week and muscle-strengthening activities two or more days a week. When you are active, your cells become more sensitive to insulin and work more efficiently. The American Diabetes Association has more information on the importance of exercise for preventing and managing diabetes here.
Eat Right - Since diabetes is essentially too much sugar in your blood, being smart about sugar consumption is important. Added sugar is in everything from yogurt to pasta. You may be eating more sugar then you realize since it is not just in cakes and cookies anymore. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables keeps things balanced.
Living with Diabetes
Over the last several decades, rates of serious complications among people with diabetes are declining. Patients with diabetes are living longer and healthier lives thanks to better control of blood sugar, new treatment strategies, and improved management of co-existing conditions such as high blood pressure.
The National Institute of Health (NIH) offers these four key steps to help control diabetes.
Step 1: Learn About Diabetes
Become educated on the types of diabetes and how to manage the disease.
Step 2: Know Your Diabetes ABCs
Monitor and manage A1C (blood glucose or sugar), Blood pressure, and Cholesterol to help decrease chances of heart attack, stroke, and other diabetes problems.
Step 3: Manage Your Diabetes
Create a self-care plan and work with a health care team to reach your ABC goals. Patients are often asked to take glucometer readings 1-2 times a day to monitor the level of glucose in their blood, often before and after meals.
Step 4: Get Routine Care to Avoid Problems
Working with a physician and dietitian is very important, especially for those with type 2 diabetes. Creating a meal plan to determine how much carbohydrates, fats and proteins should be consumed each day, and at which times, helps keep levels of sugar in the blood steady. Medications such as insulin may be provided if blood glucose levels remain high. See your health care team at least twice a year to find and treat any problems early.
In addition, individuals at risk for developing diabetes should:
- Check the skin and bones on your feet/legs
- Watch for numbness of the feet
- Check cholesterol and blood pressure often
- Participate in kidney and eye tests with your physician
- Visit the dentist at least every 6 months
Return to top...


Below is a compilation of resources and websites about diabetes. Check out the "Understanding Diabetes" video for a comprehensive overview of diabetes, inspiring stories from those managing their disease as well as healthy eating tips and motivating exercise demonstrations here.
RESOURCES
- American Diabetes Association - A comprehensive website providing educational information on all types of diabetes, including the latest in medical research and advice for living with diabetes.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases - A resource for understanding more about diabetes, resulting health complications, as well as the latest in clinical trials.
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation - Provides focused information on type 1 diabetes, additional resources and the latest developments in research.
- National Eye Institute - A resource for diabetic eye disease and other sight related diseases.
- American of Nutrition and Dietetic - A website dedicated to teaching all ages about nutrition and healthy eating, provides recipes as well.
- National Kidney Foundation - A complete resource for information on kidney disease, including latest development in research.
- Type 1 Diabetes International Clinical Trial Net -This website offers risk screening for relatives of people with type 1 diabetes and information on innovative clinical studies to preserve insulin production.
- Bracelets or neck chain emblems with personal medical information - A source for medical IDs such as MedicAlert bracelets.
- Children with diabetes online community - An online community for kids, families and adults with diabetes.
Return to top...